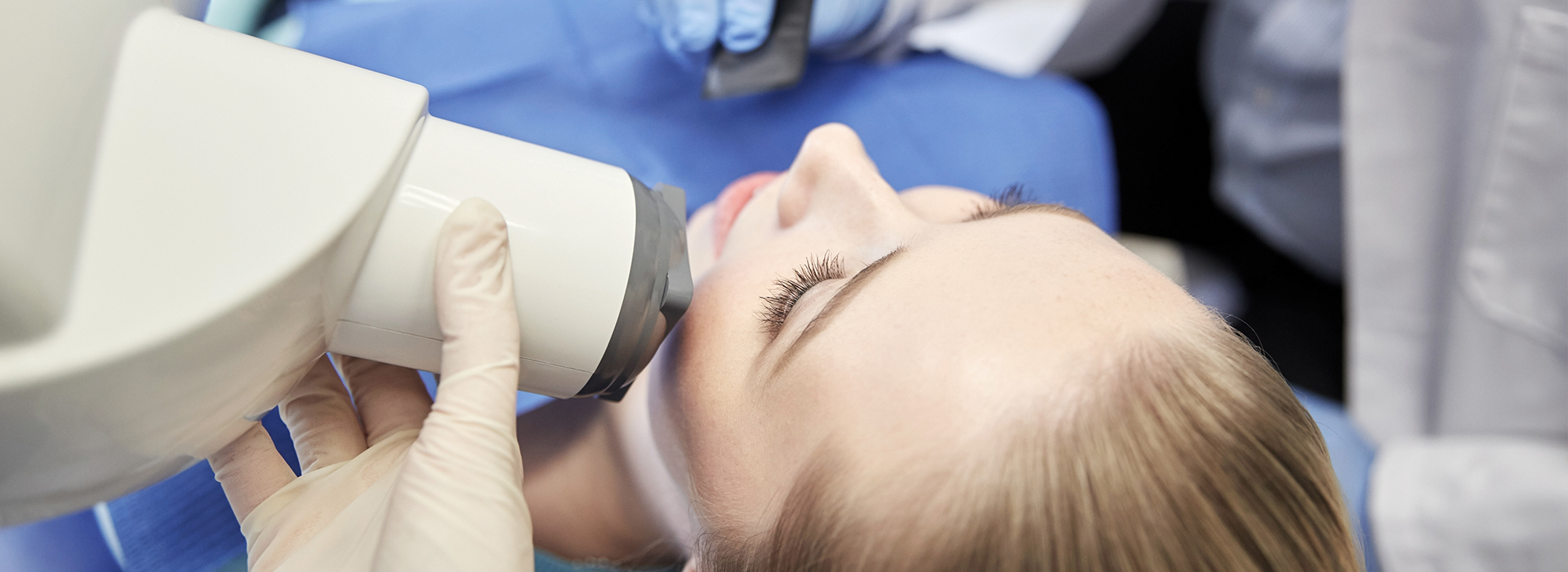
How modern digital sensors capture detailed images
Digital radiography replaces traditional film with electronic sensors that detect X-ray photons and convert them into digital signals. Instead of waiting for chemical development, these sensors create images that are immediately available on a computer screen. The digital file format allows clinicians to adjust contrast, zoom in on areas of interest, and compare images side-by-side without degrading image quality — tools that are invaluable when assessing hard-to-see issues in teeth and supporting bone.
There are two common sensor types used in dental digital radiography: intraoral sensors that fit inside the mouth for periapical and bitewing views, and extraoral detectors used for panoramic or cone beam imaging. Both capture the fine anatomical detail clinicians need to evaluate decay, root structures, and bone levels. The clinical workflow is streamlined because images are produced in seconds and stored directly within a patient’s electronic record.
Because the image is created and displayed digitally, clinicians can enhance and annotate radiographs to clarify findings for patients and other members of the care team. These enhanced views support precise treatment planning and help patients understand recommended care without relying on memory or verbal description alone. The result is more informed decision-making and clearer communication throughout the treatment process.
Safer imaging: reducing radiation without sacrificing detail
One of the most important advantages of digital radiography is the reduced radiation dose compared with conventional film. Digital sensors are more efficient at capturing X-ray photons, so diagnostic-quality images can often be produced with less radiation. This improvement is especially meaningful for patients who require periodic monitoring or those with conditions that necessitate frequent imaging.
Modern systems also include exposure controls and image optimization algorithms that help minimize unnecessary repeat exposures. Proper sensor placement, up-to-date equipment, and adherence to best-practice imaging protocols further reduce patient exposure while preserving the diagnostic information clinicians need. In short, digital radiography achieves a balance between safety and image clarity.
Dental teams follow established radiation-safety guidelines to ensure every image taken is justified and optimized for the clinical question at hand. For vulnerable populations, including children and pregnant patients, those guidelines inform decisions about timing, technique, and the use of protective measures. The overall aim is consistent: obtain the information necessary for high-quality care with the lowest reasonable exposure.
Sharper diagnostics: what high-resolution images reveal
High-resolution digital images enhance a clinician’s ability to detect early-stage problems that might be missed on lower-quality film. Subtle areas of decay, early bone loss, internal root issues, and cracks in teeth are more readily apparent when clinicians can manipulate image contrast and magnification. This earlier detection often leads to simpler, less invasive interventions and better long-term outcomes.
Digital radiography also improves the assessment of restorative work and implant sites. Accurate evaluation of margins, contact points, and surrounding bone can influence treatment decisions and follow-up care. When comparing serial images over time, clinicians can more reliably track changes in anatomy, healing, or disease progression because digital files are consistent and reproducible.
Advanced image-processing tools — such as edge enhancement and noise reduction — support diagnostic confidence without introducing clinical bias. These tools augment a trained clinician’s judgment by clarifying structures that are relevant to diagnosis and treatment planning, while the final clinical decision remains rooted in professional evaluation and examination findings.
Streamlined care: faster results and better collaboration
Digital files integrate directly into electronic health records, which speeds documentation and reduces administrative steps. Images are instantly accessible to the treating clinician at chairside, enabling efficient case presentation and real-time discussion of findings with the patient. The rapid turnaround shortens appointments, clarifies treatment options, and supports informed consent conversations in the moment.
Because digital radiographs are easily shared, specialists and referring providers can view the same images without delay. Secure electronic transfer facilitates coordinated care for complex cases, second opinions, or interdisciplinary treatment planning. This connectivity helps ensure everyone involved in a patient’s care is working from the same, high-quality visual information.
From a practice operations perspective, digital imaging reduces the need for physical storage and the time associated with locating and copying film. Staff can retrieve past images with a few clicks, freeing clinical time for patient care. The organization and accessibility of a digital archive also support long-term monitoring and efficient recordkeeping that protects continuity of care.
A better experience for patients and the environment
Patients frequently appreciate the comfort and convenience of digital radiography. Intraoral sensors are designed to be smaller and more ergonomic than traditional film holders, which can make positioning quicker and less intrusive. Instant image review at the chair helps patients visualize findings rather than relying on verbal explanations, which improves understanding and engagement in the care process.
Digital imaging is also more environmentally friendly than film-based systems because it eliminates the need for chemical developers and paper-based storage. Removing these consumables reduces waste and reduces the practice’s environmental footprint. Many practices choose digital systems as part of broader efforts to adopt sustainable clinical operations.
At our offices, investment in up-to-date imaging technology reflects a commitment to quality, safety, and patient-centered care. By combining advanced diagnostic tools with clear communication and a focus on patient comfort, the practice aims to make imaging an informative and reassuring part of every visit.
Summary and next steps
Digital radiography is a modern, efficient approach to dental imaging that offers faster results, clearer diagnostic information, and reduced radiation exposure compared with traditional film. Its benefits extend from improved clinical decision-making to enhanced patient communication and better coordination with other providers. The environmental and operational advantages further support a practice-focused model of care.
If you would like to learn more about how digital imaging is used during dental visits or how it supports treatment planning at Cruzin' Dental, please contact us for more information.